Medical cannabis is used today as a broad term for products containing either parts of the cannabis plant, active substances from the cannabis plant or synthetically produced cannabinoids. The medical cannabis products are used to relieve a variety of diseases, including sclerosis, nerve pain and cancer. Medical cannabis is available in a variety of forms, including cannabis oil, capsules, tablets, dried cannabis flowers and oral cavity spray.



In Denmark, it is legal and possible to obtain medical cannabis. Medical cannabis must be prescribed by a doctor and can only be dispensed from a pharmacy or a hospital. The legal medical cannabis products are standardised and controlled. All products comply with the Danish Medicines Agency’s rules and are therefore the patients’ guarantee that they will receive a clean and uniform product every time.
Non-prescription medical cannabis is illegal and may contain harmful substances. There is considerable uncertainty about how illegal cannabis medication is made and what the products actually contain. The illegal cannabis products from the illegal market may contain something quite different from what is stated on the package, and the contents may vary from product to product. The manufacturing process and the products are not controlled and are not subject to the rules of the Danish Medicines Agency. Many of the products from the illegal market are produced to promote intoxication and not the plant’s therapeutic positive potential. There are many indications that illegal cannabis has become highly potent, which can lead to an over-effect on the patient, which inhibits efficacy and, at worst, can aggravate the underlying disease and cause side effects.
In Denmark, patients can access medical cannabis in 4 ways:
- The medical cannabis pilot programme Medical cannabis products under the pilot programme are either grown and produced in Denmark or imported as finished products from abroad. Medical cannabis under the pilot programme can be prescribed by a doctor for all patients and all diseases. On the Danish Medicines Agency’s website you can see a list of admitted cannabis products for medical use under the pilot programme click here
- Approved medicine One drug based on cannabis has been approved in Denmark. It is the drug called Sativex (approved 2011). Sativex is an oral cavity spray for treatment of multiple sclerosis spasms. Sativex contains cannabis extracts. Sativex is prescribed by specialists in neurology to patients with multiple sclerosis.
- Unauthorised medicine on compassionate use permit Other countries, e.g. the United States, have approved the drugs Marinol and Nabilone (approved 1985) containing synthetically produced cannabinoids. If a Danish doctor wishes to prescribe these two products to a patient, the doctor must apply for a compassionate use permit from the Danish Medicines Agency. If the Danish Medicines Agency approves the doctor’s application, the drug may be imported to the patient.
- Magistrally manufactured medicine with cannabis Magistrally manufactured medicine with cannabis is prepared at the Glostrup pharmacy for each patient following a doctor’s prescription.



What does the cannabis plant contain?
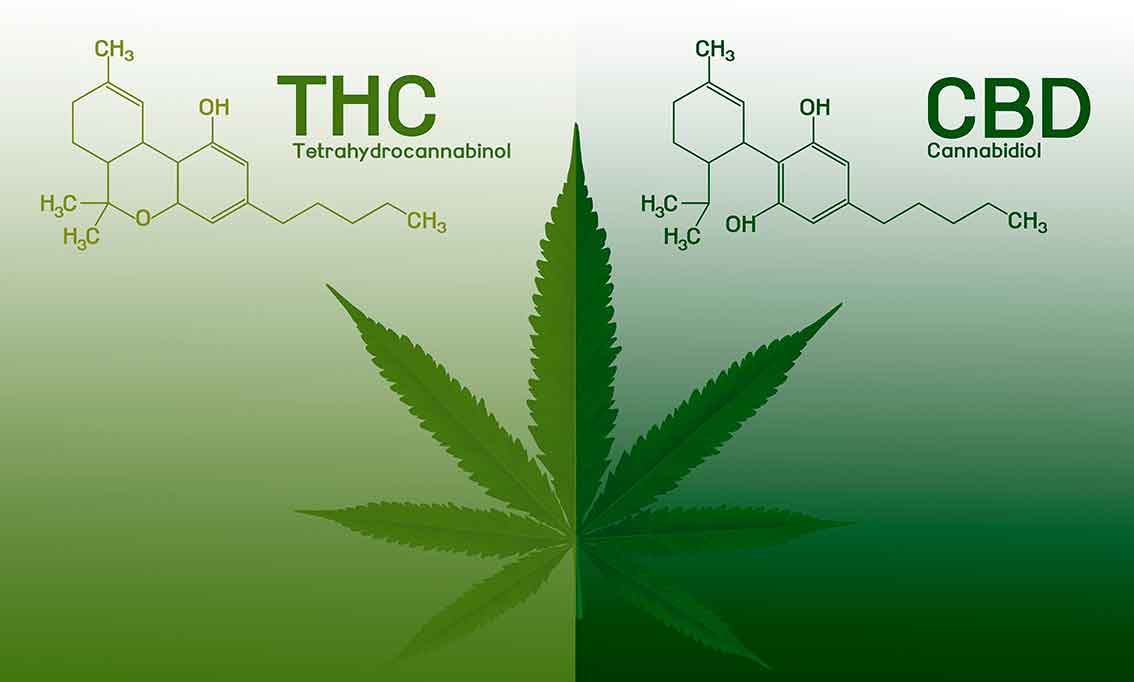
The cannabis plant contains many different active substances called “cannabinoids”. The most important active and commonly known cannabinoids are CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol). CBD, unlike THC, is not a psychoactive substance and therefore does not have a euphoric effect.
The cannabis plant also contains terpenes and flavonoids. Medical cannabis from the cannabis plant therefore contains many different substances. Medical cannabis from the cannabis plant works by a phenomenon called the entourage effect. This means that the effect of one substance is influenced by its entourage, i.e. all the components with which it is accompanied.
What is the pilot programme?
On 15th December 2017, the Danish Parliament passed the “Act on a Medical Cannabis Pilot Programme”. The purpose of the pilot programme is to give patients legal access to medical cannabis treatment if they have not benefited from approved conventional medicine. In this way, patients who self-medicate with illicit products have a legal alternative, and at the same time the treatment take place under regulation and supervision of health professionals.
The Pilot Programme also allow Danish cultivation and production of medical cannabis products. Companies can be licensed by the Danish Medicines Agency to cultivate, produce, sell and export medical cannabis materials and finished products.
The intention is that the pilot programme should provide a better basis for assessing the use of medical cannabis. The pilot programme, which came into force on 1st January 2018 was initially planned for a four-year period. However, the Parliament has decided to extend the Pilot with another four-year period – meaning the Pilot Programme is due to end in December 2025.
The Pilot Programme is managed and controlled by the Danish Medicines Agency, which is also responsible for granting licenses to companies that wish to cultivate, produce, import or export and distribute legal medical cannabis products.
With the “Pilot Programme” medical cannabis was legalised for dispense from a pharmacy where a doctor has issued a prescription to the patient. It is still not legal to buy medical cannabis on the Internet and in stores neither in Denmark nor from abroad unless prescribed by a doctor.
Who can get a prescription for medical cannabis under the pilot programme?
Based on a medical assessment, it is now possible to treat patients, who wish to try medical cannabis.
The doctor has the right of prescription for the products included in the pilot programme, which means that medical cannabis can be prescribed for all patients regardless of disease. Conversely, no doctor has a duty to prescribe medical cannabis.
Although it is possible to prescribe medical cannabis to all patients regardless of disease, the Danish Medicines Agency has made an assessment of the patient groups and possible therapeutic indications that could be relevant for medical cannabis treatment:
– Painful spasms caused by multiple sclerosis
– Painful spasms caused by spinal cord damage
– Nausea after chemotherapy
– Neuropathic pain, i.e. pain due to a disease of the brain, spinal cord or nerves.
The Danish Medicines Agency indicates that treatment with medical cannabis should only be attempted if the patient has tested relevant approved medicine without satisfactory results.
Furthermore, the Danish Medicines Agency clearly recommends not to treat children and young people under the age of 18 with medical cannabis.
If the doctor doesnot wish to prescribe medicial cannabis, he may choose to refer the patient to a pain clinic experienced in medical cannabis for patients.
If your doctor does not wish to prescribe medical cannabis or to refer you to a pain clinic, there are several options. The choice of doctors and hospitals is free, which means that patients can consult another doctor if the patient so wishes.
There is also the option of going to a pain clinic or a private practice neurologist. They can help provide an additional assessment of whether medical cannabis may help you. However, not all pain clinics and private practice neurologists will prescribe medical cannabis, which means that it is a good idea to investigate how they relate to medical cannabis before making an appointment. If you choose to go to a pain clinic or private practice neurologist, it will be an advantage if you can get a referral from your doctor or neurologist. The referral will cover the expenses that are otherwise incurred when you go to a private doctor. If you do not get a referral, you have to pay for the consultations yourself.
Read more about the Danish Medicines Agency’s assessment of patient groups and possible therapeutic indications here.

Who can get a reimbursement for medical cannabis under the pilot programme?
On 1st January 2019, a special medical cannabis reimbursement scheme covered by the 4-year medical cannabis pilot programme was introduced. The scheme applied retroactively for purchases made from 1st January 2018.
Citizens, who are terminally ill, will be reimbursed at 100%. Other citizens will be reimbursed at 50% for an annual consumption of medical cannabis that does not exceed DKK 20,000. When the total consumption exceeds DKK 20,000, no reimbursement is granted, e.g. after DKK 20,000 the total price of the product is at own contribution. Reimbursement for purchases from 1 January 2019 is automatically deducted at the pharmacy at the moment of dispense.
You can read more about the special medical cannabis reimbursement scheme on the website of the Danish Medicines Agency click here.
The doctor’s prescription of medical cannabis in the pilot programme is the central premise for receiving a reimbursement
Can I get extra reimbursement if I am a member of health insurance "danmark"?
Health insurance “danmark” also grants reimbursement for medical cannabis in the pilot programme.
If you are a member of group 1 or group 2, you will receive a reimbursement of 50% and you will receive a reimbursement of 25% if you are a member of group 5.
Read more about calculating the reimbursement for medicines click here.
Medical cannabis and driving
When a patient is treated with medical cannabis, it can affect the ability to drive. Therefore, the doctor has an important role in assessing whether the patient is able to drive a car safely despite the treatment.
The Danish Patient Safety Authority has a number of recommendations for physicians, who are to consider any driving bans for patients receiving cannabis-based medicines.
Read the Danish Patient Safety Authority’s recommendations click here.



Medical cannabis when travelling
At Copenhagen Airport CPH you can read about what to do when taking prescription medicine and going travelling click here.
At borger.dk you can read about what to do when taking prescription medicine and going travelling click here.
At apoteket.dk you can also read about what to do when taking prescription medicine and going travelling click here.
On their website, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs has also written about medicine on the journey click here.
What is the endocannabinoid system?
The endocannabinoid system is a natural signalling system not only found in humans but present in all vertebrates. It is vital for maintaining human health.
Back in the 1960s, the Israeli scientist Dr. Raphael Mechuolam identified the chemical structures of two of the main components of the cannabis plant, the active substances delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Since then, over 80 active substances have been identified in the plant, which are commonly referred to as cannabinoids, but research has mainly focused on THC and CBD.
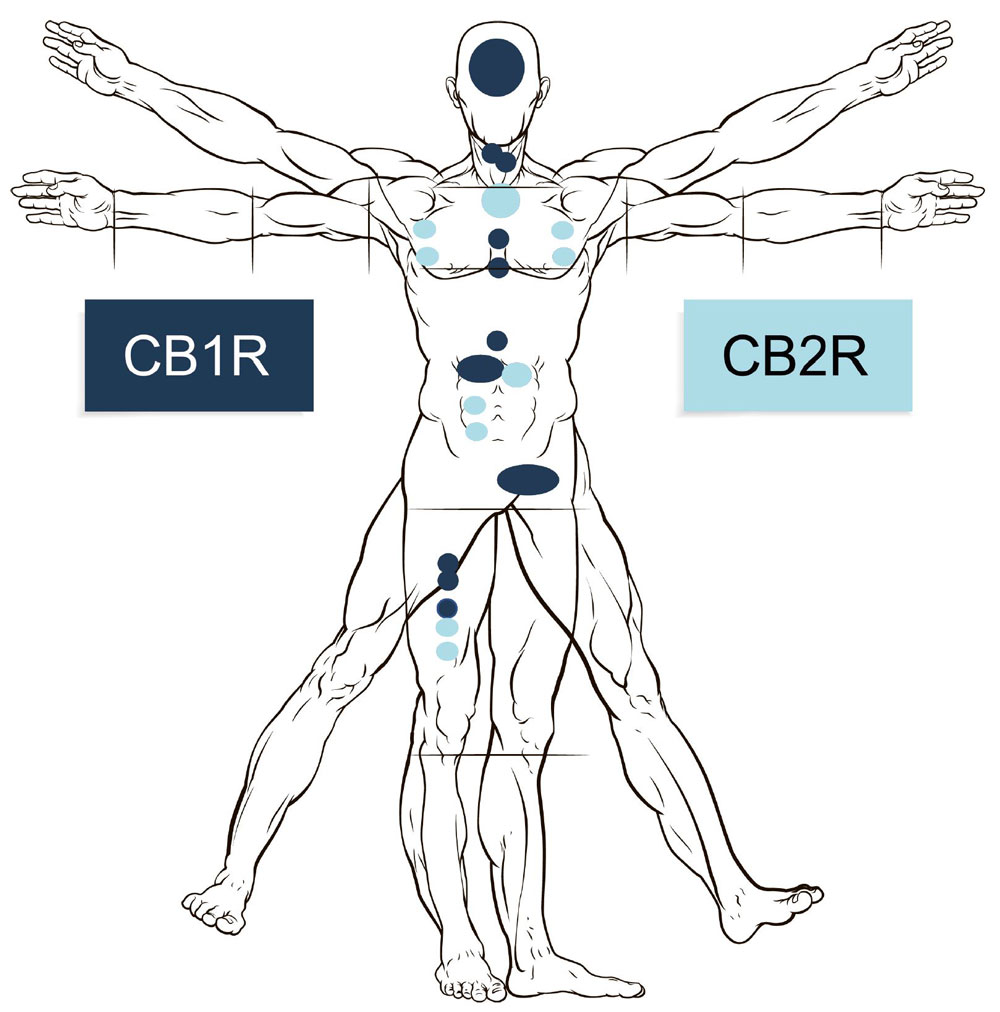
In the late 1980s, researchers identified the receptors onto which the substances act in humans. The CB1 receptors were located primarily in the brain and other parts of the central nervous system, and the influence of these cannabinoid receptors initiates the euphoric effect of THC. The CB2 receptors are located in other parts of the body in relation to cells involved in our immune system.
The endocannabinoid receptors are widely distributed throughout the body; in the brain, the organs, the intestinal system, the connective tissue, the glands and the immune cells.
In the 1990s, researchers identified the body’s own signalling substances, the inner cannabinoids, which act on the cannabinoid receptors. Thus, the body itself creates cannabis-like substances that bind to the CB1 and CB2 receptors.
The CB1 and CB2 receptors, the inner cannabinoids and the substances that degrade them, together form the human endocannabinoid system.
The endocannabinoid system is involved in a wide variety of different processes in the body. Cannabinoids are involved in appetite, blood pressure, blood flow to the brain, digestion, nausea, the immune system, inflammation, memory, mood, movement, pain, reproduction and stress. The endocannabinoid system is one of the most important physiological systems involved in establishing and maintaining human health. The endocannabinoid system is not yet fully identified.
In people, who have a chronic course of disease, the cannabis plant is increasingly used for self-medication. The problem is that the illegal market produces cannabis for the purpose of promoting intoxication and not for its treatment potential. Many factors indicate that street-level cannabis has become highly potent, which means it may over-affect the endocannabinoid system, thereby inhibiting the endocannabinoid system’s functioning and exacerbating an underlying disorder.
The cannabis plant has a potential in the treatment of both mental and physical disorders. It has recently been discovered that the non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD) can improve the functioning of the endocannabinoid system and increase its own production of the cannabinoid anandamide (the chemical substance produced by the brain itself and which can activate CB1 and CB2 receptors is called Anandamide) without creating tolerance. It is therefore possible that we can use parts of the cannabis plant in our efforts to regulate the endocannabinoid system.
The discovery of the functioning of the endocannabinoid system in humans seems to support the extensive anecdotal evidence found in the soothing effects of cannabis on a host of disorders.